(WOODLAND HILLS, CA) – The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI), a non-profit research organization devoted to developing bioengineered systems, devices, and technology for biomedical applications, held a Grand Opening celebration at their newest research facility in Woodland Hills. The event drew almost 100 guests, which included local dignitaries, members of the Terasaki family, TIBI faculty and staff, and members of the building’s design and construction teams.
News
News
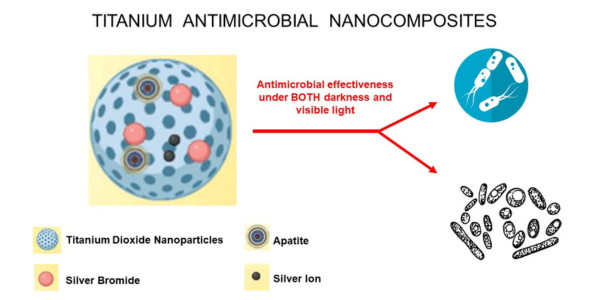
(LOS ANGELES) - Scientists from the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) have chemically modified titanium dioxide nanoparticles to render them with antimicrobial powers when exposed to both darkness and visible light. These composite nanoparticles, studded with selected chemicals, demonstrated antibacterial and antifungal effectiveness, while serving as models to elucidate the pathways by which these effects are achieved. This opens enticing possibilities for green technology applications, such as wastewater treatment, air purification, or preservation of food.
Improvements made possible with strategic chemical modifications
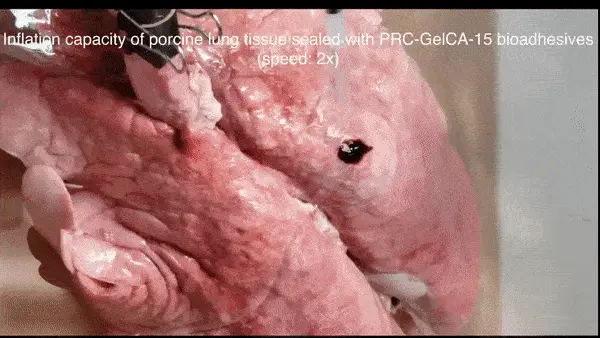
(LOS ANGELES) – As part of a collaborative effort, scientists from the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) have employed inventive chemistry to produce an injectable biomaterial with significantly improved adhesive strength, stretchability, and toughness. This chemically modified, gelatin-based hydrogel had attractive features, including rapid gelation at room temperature and tunable levels of adhesion. This custom-engineered biomaterial is ideal as a surgical wound sealant, with its controllable adhesion and injectability and its superior adherence to a variety of tissue and organ surfaces.
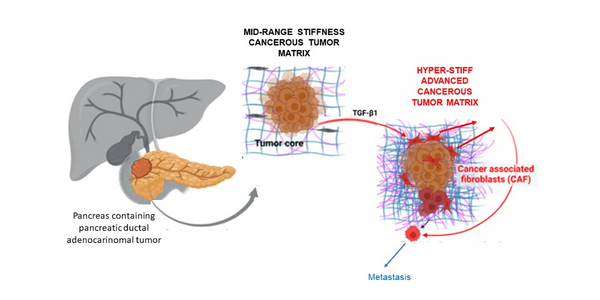
(LOS ANGELES) – Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), is highly aggressive and lethal. It is the most prevalent type of pancreatic cancer, making up 90% of cases; it also has a high rate of metastasis, with an average five-year survival rate of less than 10%.
(LOS ANGELES) – A collaborative team from the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) has developed a contact lens prototype that is specifically designed to prevent contact lens-induced dry eye (CLIDE). The lens alleviates this condition by facilitating tear flow in response to normal eye blinking. This approach can relieve the discomfort, visual impairment, and risk of inflammation experienced by millions of contact lens users suffering from CLIDE.
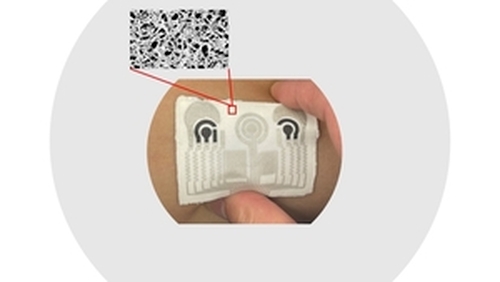
(LOS ANGELES) – Scientists from the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) have devised a first-of-its-kind electronic skin (E-skin) patch for advanced healthcare monitoring. With an optimum choice in materials coupled with a novel fabrication method, their unique E-skin patch provides simultaneous, continuous monitoring of multiple bodily parameters while also providing temperature-moisture management and breathability.
(LOS ANGELES) – As outlined in their recent publication in Biomaterials Science, researchers from the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation, (TIBI), have developed an injectable, temperature sensitive, shear-thinning hydrogel (T-STH) hemostat that works rapidly at body temperature to stop bleeding from a wound. This technology allows anyone to treat victims of traumatic injuries immediately and effectively. Once patient stability is achieved, the T-STH hemostat can easily be removed using a cold saline wash without leaving residues or causing re-bleeding of the wound. The saline wash also allows for removal of any debris lodged into the wound.
The new year will bring excitement and new opportunities for the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI). The long-awaited final construction of TIBI’s new 50,000 square foot facility in Woodland Hills is due for completion near the end of 2022, and employees will be moving in during the month of January 2023.